A huge asteroid hurtling through space at 63,000mph could one day hit Earth causing "immense suffering and death", astronomers say.
The space rock was discovered in 1999 and is likely to blast in between the Earth and the moon in 2135 - a little too close for comfort.
But on a return trip later in the century, it is estimated the asteroid known as 101955 Bennu could actually strike our planet.
Dante Lauretta, the NASA expert in charge of a new mission to analyse the asteroid, said: "That 2135 fly-by is going to tweak Bennu's orbit, potentially putting it on course for the Earth later that century.
It is due to hurtle between Earth and the moon in 2135
"We estimate the chance of impact at about one in 2,700 between 2175 and 2196.
"It may be destined to cause immense suffering and death."
But he added that there's a very good chance that science will be so advanced by then that it could be knocked off course, saving humanity.
The team puts the finishing touches to the spacecraft. Pic: NASA
"Don't run out and buy asteroid insurance," he said, explaining that "nukes" or a "gravity tractor" could be among the options for knocking it off course.
"I wish I could be around in 2135 to see what happens," he added.
The asteroid measures 500m across, and a space rock of that size is - on average - expected to hit the Earth every 130,000 years.
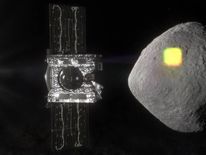
An artist's impression of how the operation will look. Pic: NASA
The force of Bennu striking the Earth would be the equivalent of three billion tons of high explosive being detonated.
A spacecraft is being launched by NASA to scan the surface of the asteroid, and harvest samples from its surface.
As most asteroids predate the formation of planets, scientists hope the information gleaned will help them to better understand the building blocks of life.
But by better understanding the make-up of the asteroid, they will also hopefully be a step closer to working out how to avoid a potential collision.




No comments:
Post a Comment